A Comprehensive Guide to AEM Cloud Service Architecture
Gain insights into AEM Cloud Service architecture with this comprehensive guide to optimize your enterprise solutions
Table of Contents
Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) has been a favorite Content Management System (CMS) for big businesses for quite some time. Well known brands like AT&T, JP Morgan Chase & Co., and UnitedHealth Group rely on it for managing their content daily.
But, as businesses grow and technology changes, managing content becomes much trickier. That's why Adobe introduced AEM as a Cloud Service (AEMaaCS) in 2020. This move aimed to solve some tough problems faced by traditional AEM users, especially the headache of scaling up infrastructure to keep pace with growth.
Still, using AEMaaCS is a complex setup that can be tough for those trying to integrate it into their workflow. For this reason, we want to explore its features and functions while tackling the challenges of using this cloud-based CMS.
AEM Architecture: A Basic Overview
AEM has several integral tiers, each serving a purpose in the content lifecycle:
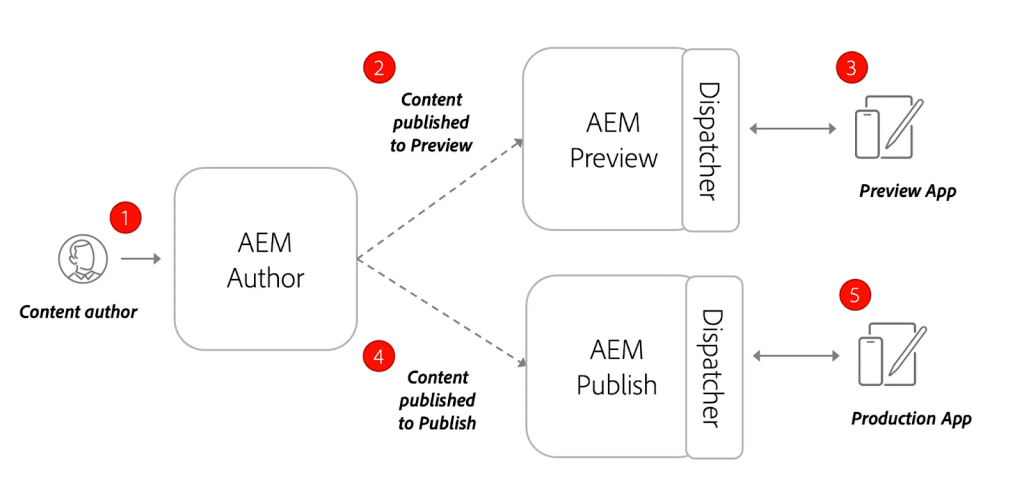
Author: At the core of AEM, the Author tier is where content creation and management take place. This is where web pages are crafted, updated, and enriched with media content. Content authors and editors use intuitive interfaces to develop and maintain digital experiences.
Preview: Before content goes live, it undergoes thorough scrutiny in the Preview tier. Here, content creators and stakeholders review and validate the content's appearance and function to ensure a flawless user experience. The Preview tier acts as a staging environment, showing how content will appear once published.
Publisher: The Publisher tier is the public-facing aspect of AEM, where all published content is. It is the gateway through which end-users access the finalized web content. The Publisher tier ensures that content is efficiently delivered to audiences across various channels and devices.
Dispatcher: The Dispatcher focuses on optimizing web performance and enhancing user experience. It helps manage incoming requests efficiently and direct them to appropriate servers. Key tasks the Dispatcher performs include caching frequently accessed content to expedite delivery and load balancing to evenly distribute network traffic, preventing server overload and ensuring great performance.
AEM as a Cloud Service Architectural Differences
Transitioning from traditional on-premise setups to AEMaaCS brings significant architectural differences, revolutionizing how enterprises manage and deliver content.
Here's a breakdown:
Automatic Updates: Under AEMaaCS, automatic updates are in place through integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. This ensures that the software is always up to date, with new feature releases occurring monthly and maintenance updates, including important security patches, deployed daily.
Authentication: AEMaaCS simplifies authentication by pre-configuring Adobe Identity Management System (IMS), which uses the OAuth protocol. This authentication process enhances security and user management capabilities.
Publication Process: Content delivery in AEMaaCS is facilitated through Apache Sling, providing a framework for efficient content distribution to the public. This guarantees excellent performance and dependability when delivering digital experiences to users.
Development: Developers' workflows are revamped in AEMaaCS, with restricted access to CRX/DE and read-only access to the Open Service Gateway Initiative (OSGi) console. Application code and configurations are managed within the Git code repository of the associated Cloud Manager program, emphasizing collaboration and version control.
Operations and Performance: AEMaaCS introduces automated maintenance tasks, such as indexing and backups, reducing manual intervention and enhancing operational efficiency. The architecture incorporates health checks to monitor node health, swiftly replacing unhealthy nodes to maintain service availability.
Scalability: Unlike traditional AEM setups, AEMaaCS offers infinite scalability across author, publisher, and dispatcher tiers, ensuring effortless expansion to accommodate evolving business needs and growing digital footprints.
AEM Sites: While retaining core functions, AEMaaCS introduces new features like asynchronous page operations and a revamped AEM reference site. Along with this, a clear separation of the AEM repository into mutable and immutable code enhances agility and maintainability.
Key AEM as a Cloud Service Features
DevOps With Cloud Manager: Cloud Manager gives businesses scalable DevOps capabilities, offering autoscaling, flexible deployment modes, and streamlined management of AEM environments.
Application Automation: Developers can use automation capabilities to streamline repetitive tasks, enhancing productivity and accelerating development cycles.
Built-in CDN: AEMaaCS incorporates a built-in Content Delivery Network (CDN), ensuring rapid and efficient content delivery, even at scale, to enhance user experiences globally.
Dynamic Architecture: By abstracting infrastructure concerns and enabling autoscaling, AEMaaCS has a dynamic architecture that adapts to fluctuating workloads and evolving business demands.
Automated Testing: Integrated automated testing capabilities scan for common vulnerabilities, ensuring proactive threat detection and mitigation to bolster security posture and reduce risks.
Adobe Integration: AEMaaCS integrates with other Adobe tools, including analytics and marketing products, enabling holistic digital experience management and optimization.
But, despite the numerous benefits offered by AEMaaCS, certain challenges have been found, both inherited from traditional AEM deployments and newly introduced:
Common Challenges With AEM as a Cloud Service
Security Challenge: While the cloud offers scalability and flexibility, it also introduces security concerns that should be addressed immediately. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with industry regulations remain top priorities for enterprises using AEMaaCS.
Integration Challenge: Integrating AEM with existing systems and third-party applications can be complicated and requires meticulous planning. Thorough and careful integration is important for optimizing workflows and delivering cohesive experiences across channels.
Learning Curve Challenge: AEM, whether on-premise or as a cloud service, can be quite complicated to learn. Understanding its intricate features and workflows requires time and effort, potentially hindering rapid adoption and efficiency.
Reliance on Developers Challenge: Due to AEM's complexity, many teams rely heavily on developers for content updates and modifications. This dependency on technical expertise can lead to bottlenecks and hinder agility in content management processes.
Limited Customization Challenge: While AEM offers customization capabilities, the platform imposes limitations, especially compared to open-source alternatives. Enterprises may be constrained in achieving highly tailored solutions to meet their specific requirements.
An Alternative to AEM: WordPress
Looking for an alternative? WordPress is a popular option, offering several advantages:
Integration Capabilities: WordPress is an open-source platform with extensive integration capabilities. It enables interoperability with various systems and applications. Its flexibility allows enterprises to create cohesive digital ecosystems tailored to their needs.
Market Dominance: WordPress dominates the CMS market. While AEM only has a 5.3% share of the top 1,000 sites, WordPress has a staggering 46.7%. Its widespread adoption attests to its versatility and suitability for enterprise-level organizations seeking scalable and reliable content management solutions.
User-Friendly Interface: WordPress prioritizes user experience, providing an intuitive interface that allows content creators to easily author and publish content without extensive technical expertise. This democratization of content management enhances efficiency and agility within organizations.
Extensive Customization: WordPress offers customization options unlike any other, allowing businesses to tailor their digital experiences to align with brand identity and unique requirements. Its vast ecosystem of themes and plugins facilitates rapid development and customization, fostering innovation and differentiation.
Robust Community Support: With a vast community of developers and enthusiasts, WordPress offers support and resources not seen elsewhere. Businesses can benefit from ongoing updates, security patches, and knowledge-sharing opportunities to ensure long-term stability and resilience.
Migration from AEM to WordPress can be tough, but with the help of professionals, you can have your site ready in no time!
Take the Next Step With Multidots’ Expertise
As we’ve seen, AEMaaCS can be an effective way to manage your content. However, it's equally important to recognize that WordPress offers the same strengths and has its own advantages.
Multidots, a web development agency and WordPress VIP Gold Partner, is known for its expertise in enterprise migrations. We can help you take the next step to using WordPress's full power.
Multidots is unmatched in its ability to create enterprise-level websites on WordPress. We provide scalability and flexibility to enhance your site's functions. Our managed migration service guarantees a smooth transition for businesses wanting to switch to WordPress, removing any concerns about losing data or experiencing operational interruptions.
Start embracing WordPress’s benefits over AEM today and unlock new possibilities for your business. Get in touch with Multidots and discover the potential of WordPress!
Feel free to schedule a quick call with our migration expert.
Contact Us
